Poster
The use of cabergoline at dry-off reduced SCC and increased milk production in a commercial dairy herd in Brazil
Authors
Carla Azevedo (Ceva Sante Animale. Libourne, France); Juan Munoz-Bielsa (Ceva Sante Animale. Libourne, France); Alexandre Souza (Cargill, Brazil)
Publication information
World Buiatric Congress 2022
OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to investigate, under Brazilian field conditions, the effect of one single administration of cabergoline at dry-off (Velactis®, Ceva Santé Animale, Libourne, France) on the somatic cell counts (SCC) and milk production of high yielding dairy cows during the subsequent lactation. Our hypothesis was that by reducing intramammary infections we would reduce SCC and therefore reduce the negative impact of mastitis on milk production.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The trial was conducted from April 2017 to September 2018, and involved 326 Holstein-Friesian dairy cows from one modern cross-ventilated commercial dairy farm in São Paulo State. Cows were enrolled in the trial if their daily milk production was equal or more than 25kg the day before dry-off. All cows were dried off abruptly and randomly assigned to one of two groups: cabergoline group received a single intramuscular injection of 5.6 mg of cabergoline (n = 168) after last milking and the control group (n=158) was left untreated. Individual SCC (log), milk production (kg), presence of subclinical mastitis (SCC ˃ 200 000 cells/mL) in the day before dry-off and dry period length were recorded for all cows. Cow’s individual SCC (log) and milk production were recorded monthly and daily, respectively, from day 7 to day 112 post-partum. Statistical analysis was performed using SAS 9.3.
RESULTS
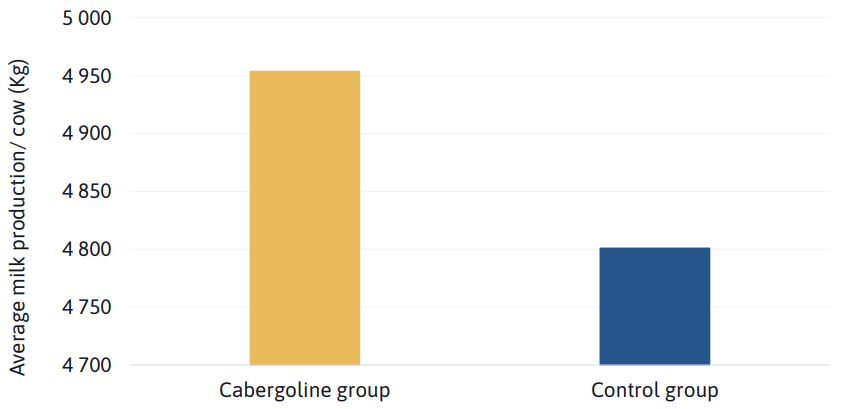
At dry-off, average log SCC (1.86 vs. 1.87), presence of subclinical mastitis (19.6% vs. 21.5%), milk production (30.4 Kg vs. 29.7 Kg) or dry period length (45.5 days vs. 45.6 days) did not differ between cabergoline and control groups, respectively (P ˃ 0.10). In the subsequent lactation, during the study period, cows treated with cabergoline presented lower log SCC compared with non-treated cows (1.57 vs. 1.77, P < 0.01). The average milk production per cow during the study period was significantly higher in cabergoline group compared to the control group (4954 kg vs. 4801 Kg, P < 0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
It is the first time that the impact of cabergoline on subsequent lactation milk production and SCC is evaluated in Brazilian commercial farms. Our data provide evidence that a single injection of cabergoline significatively reduced SCC and increased milk production in the following lactation. This is of particular interest under tropical climate where cows are undergoing severe heat stress and consequently greater SCC levels.
Don´t hesitate to read the rest of our publicatons and improve your knowledge about ruminats and their health!
Publication file:



